Cyber attacks are on the rise globally, with rise significant rise in the first quarter of 2024, almost 5% more than last time, marking an urgent need for updated ways to deal with the evolving challenges
Check Point released its cybersecurity report for the first quarter of 2024. The report shed light on the evolving cybersecurity challenges that emerged in Q4 2024 and also discussed how far the enterprises are from solving AI-powered cybersecurity challenges.
According to Check Point, a software providing company, there was a significant rise in cyber attacks, with organizations facing an average of 1308 attacks per week. This is 5% higher than the same period last year and 28% higher than the previous quarter. This increase from Q4 2023 showcases the rise in attacks and also highlights the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threat and security.
Omer Dembinsky, Data Research Group Manager at Check Point Software, said, “As we witness the dynamic landscape of cyber threats in Q1 2024, it is clear that our approach to cybersecurity needs to be equally dynamic and proactive. The significant rise and volume of cyber attacks in regions like Europe, Africa, and particularly in North America, where 59% of the known ransomware attacks were concentrated, signals an urgent need for enhanced vigilance and robust cybersecurity measures.”
“The startling 96% surge in ransomware attacks YOY on the Manufacturing sector and the unprecedented 177% increase YOY in the Communications sector are indicative of the vulnerabilities introduced by rapid digital transformation and the critical nature of these industries. These figures are not just statistics; they represent an urgent call for organizations across all sectors to bolster their defenses and prioritize cybersecurity, underscoring the need for adaptive, AI-powered defense strategies,” he added.
Industry-wise data
According to the report, the Education sector experienced the most attacks, with an average of 2454 attacks per organization weekly, followed by the Government/Military sector with 1692 attacks per week and the Healthcare sector with 1605 attacks per organization.
However, what’s concerning is the big jump in cyber attacks on hardware vendors. These attacks increased by 37% compared to last year. It shows that cyber criminals are targeting these companies more because they rely heavily on hardware for things like smart devices and the Internet of Things (IoT).
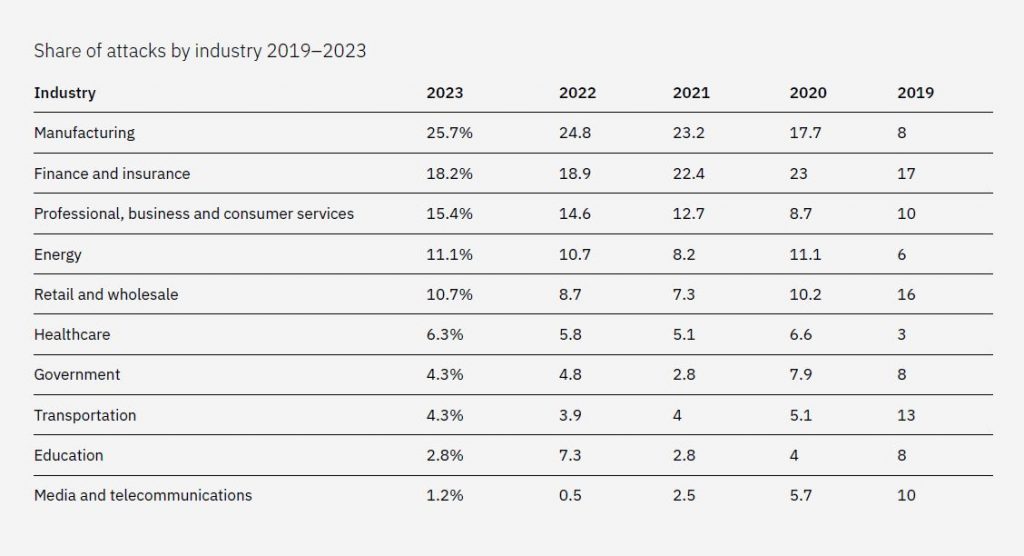
IBM X-Force Exchange, a cybersecurity threat intelligence team and platform operated by IBM, in its Threat Intelligence Index 2024, names Manufacturing as the top attacked industry in 2023 for the third year in a row, representing 25.7% of incidents within the top 10 industries year over year.
The finance and insurance industry was in second place, representing 18.2% of incidents. The share of attacks across the energy, retail and wholesale, healthcare, transportation, and arts, entertainment, and recreation sectors increased year over year.
The Communications sector saw a significant increase in attacks, likely due to rapid digital transformation and the integration of technologies like 5G and IoT.
Also read: How firms are updating their AI models for enterprises
Regional trends
According to the IBM XForce report in 2021 and 2022, the Asia-Pacific region was hit the hardest by cyber incidents, followed by Europe in second place. In 2023 Europe became the most affected region, making up 32% of incidents responded to by X-Force. North America accounted for 26% of incidents, Asia-Pacific for 23%, Latin America for 12%, and the Middle East and Africa for 7%.
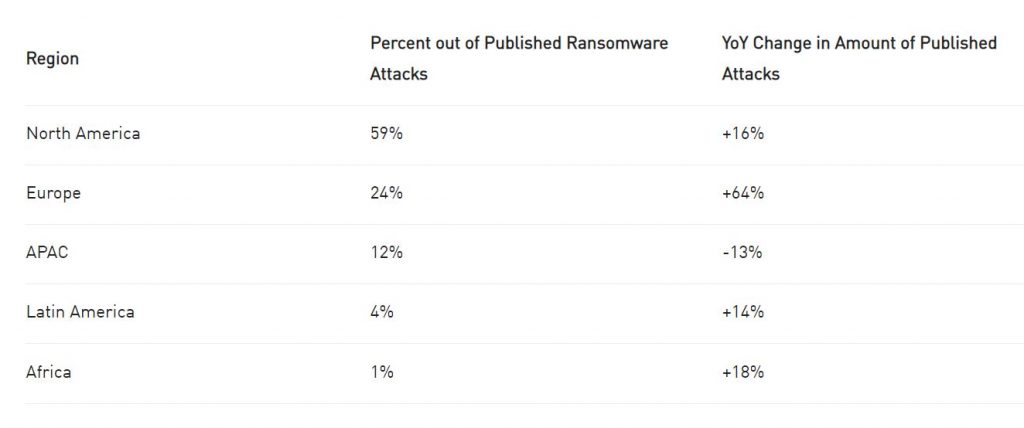
However, in the first quarter of 2024, North America faced the highest impact from ransomware attacks, with 59% out of nearly 1000 reported attacks, according to the Check Point report. Europe followed with 24%, and APAC with 12%. Europe experienced the largest increase in attacks compared to the same period in 2023, with a significant 64% rise.
This increase could be due to factors like increased digitization and regulatory environments that are making organizations more vulnerable. Meanwhile, North America saw a 16% increase, suggesting attackers continue to focus on this region.
These trends highlight the evolving cyber threat landscape and the need for robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard organizations and critical infrastructure.
What can enterprises do
Check Point suggests enterprises develop and adopt a multi-faceted approach to cybersecurity. Data backups, cyber awareness training, timely security patches, strong user authentication, and advanced anti-ransomware solutions are to be made a regular practice.
“Proactive engagement with AI-powered defenses can significantly bolster an organization’s resilience against these threats,” the report adds.
IBM states that to minimize the risk of credential harvesting attacks, enterprises should deploy Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools across all servers and workstations in their environment. These tools help detect malware, including infostealers and ransomware and can identify abnormal behavior, such as data exfiltration or unauthorized account creation. They also suggest to consider leveraging experts to establish and operationalize threat hunting within your environment.
If resources are limited, consider using AI to manage up to 85% of alerts, allowing for 24/7 threat detection and response services. Additionally, it utilizes threat intelligence to identify opportunities for mitigating new threats. Strengthen credential management practices by implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and robust password policies, including passkeys. Employ hardened system configurations to make accessing credentials more challenging.
Credential harvesting attacks often occur through phishing and watering hole attacks. Regularly educate employees on updated phishing techniques and scrutinize all third-party traffic. Treat third-party traffic as untrusted until verified. Watering hole attackers may exploit legitimate resources to deliver malware.
To reduce the cybersecurity blast radius, consider the potential impact of an incident on users, devices, or data. Implement solutions to minimize damage in case of a security incident, mainly focusing on data security and identity management.
Conclusion
Cyber attacks are evolving rapidly, faster than enterprises can keep up. This is the right time to integrate AI and leverage AI-powered tools to counter the attacks and protect businesses and the people. Enterprises need to evolve with time and technology as well, using different methods and upskilling to help ward off the pesky attacks and malware.
Image Source: Counter Point, IBM
